3.1: Introduction
Detection and attribution of climate change involves assessing the causes of observed changes in the climate system through systematic comparison of climate models and observations using various statistical methods. Detection and attribution studies are important for a number of reasons. For example, such studies can help determine whether a human influence on climate variables (for example, temperature) can be distinguished from natural variability. Detection and attribution studies can help evaluate whether model simulations are consistent with observed trends or other changes in the climate system. Results from detection and attribution studies can inform decision making on climate policy and adaptation.
There are several general types of detection and attribution studies, including: attribution of trends or long-term changes in climate variables; attribution of changes in extremes; attribution of weather or climate events; attribution of climate-related impacts; and the estimation of climate sensitivity using observational constraints. Paleoclimate proxies can also be useful for detection and attribution studies, particularly to provide a longer-term perspective on climate variability as a baseline on which to compare recent climate changes of the past century or so (for example, see Figure 12.2 from Ch. 12: Sea Level Rise). Detection and attribution studies can be done at various scales, from global to regional.
Since the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) chapter on detection and attribution1 and the Third National Climate Assessment (NCA32 ), the science of detection and attribution has advanced, with a major scientific question being the issue of attribution of extreme events. 3 ,4 ,5 ,6 Therefore, the methods used in this developing area of the science are briefly reviewed in Appendix C: Detection and Attribution Methods, along with a brief overview of the various general detection and attribution methodologies, including some recent developments in these areas. Detection and attribution of changes in extremes in general presents a number of challenges, 7 including limitations of observations, models, statistical methods, process understanding for extremes, and uncertainties about the natural variability of extremes. Although the present report does not focus on climate impacts on ecosystems or human systems, a relatively new and developing area of detection and attribution science (reviewed in Stone et al. 20138 ), concerns detecting and attributing the impacts of climate change on natural or human systems. Many new developments in detection and attribution science have been fostered by the International Detection and Attribution Group (IDAG; http://www.image.ucar.edu/idag/ and http://www.clivar.org/clivar-panels/etccdi/idag/international-detection-attribution-group-idag) which is an international group of scientists who have collaborated since 1995 on “assessing and reducing uncertainties in the estimates of climate change.”
In the remainder of this chapter, we review highlights of detection and attribution science, particularly key attribution findings for the rise in global mean temperature. However, as this is a U.S.-focused assessment, the report as a whole will focus more on the detection and attribution findings for particular regional phenomena (for example, regional temperature, precipitation) or at least global-scale phenomena that are directly affecting the United States (for example, sea level rise). Most of these findings are contained in the individual phenomena chapters, rather than in this general overview chapter on detection and attribution. We provide summary links to the chapters where particular detection and attribution findings are presented in more detail.
3.2: Detection and Attribution of Global Temperature Changes
The concept of detection and attribution is illustrated in Figure 3.1, which shows a very simple example of detection and attribution of global mean temperature. While more powerful pattern-based detection and attribution methods (discussed later), and even greater use of time averaging, can result in much stronger statements about detection and attribution, the example in Figure 3.1 serves to illustrate the general concept. In the figure, observed global mean temperature anomalies (relative to a 1901–1960 baseline) are compared with anomalies from historical simulations of CMIP5 models. The spread of different individual model simulations (the blue and orange shading) arises both from differences between the models in their responses to the different specified climate forcing agents (natural and anthropogenic) and from internal (unforced) climate variability. Observed annual temperatures after about 1980 are shown to be inconsistent with models that include only natural forcings (blue shading) and are consistent with the model simulations that include both anthropogenic and natural forcing (orange shading). This implies that the observed global warming is attributable in large part to anthropogenic forcing. A key aspect of a detection and attribution finding will be the assessment of the adequacy of the models and observations used for these conclusions, as discussed and assessed in Flato et al.,9 Bindoff et al.,1 and IPCC.10
Figure 3.1
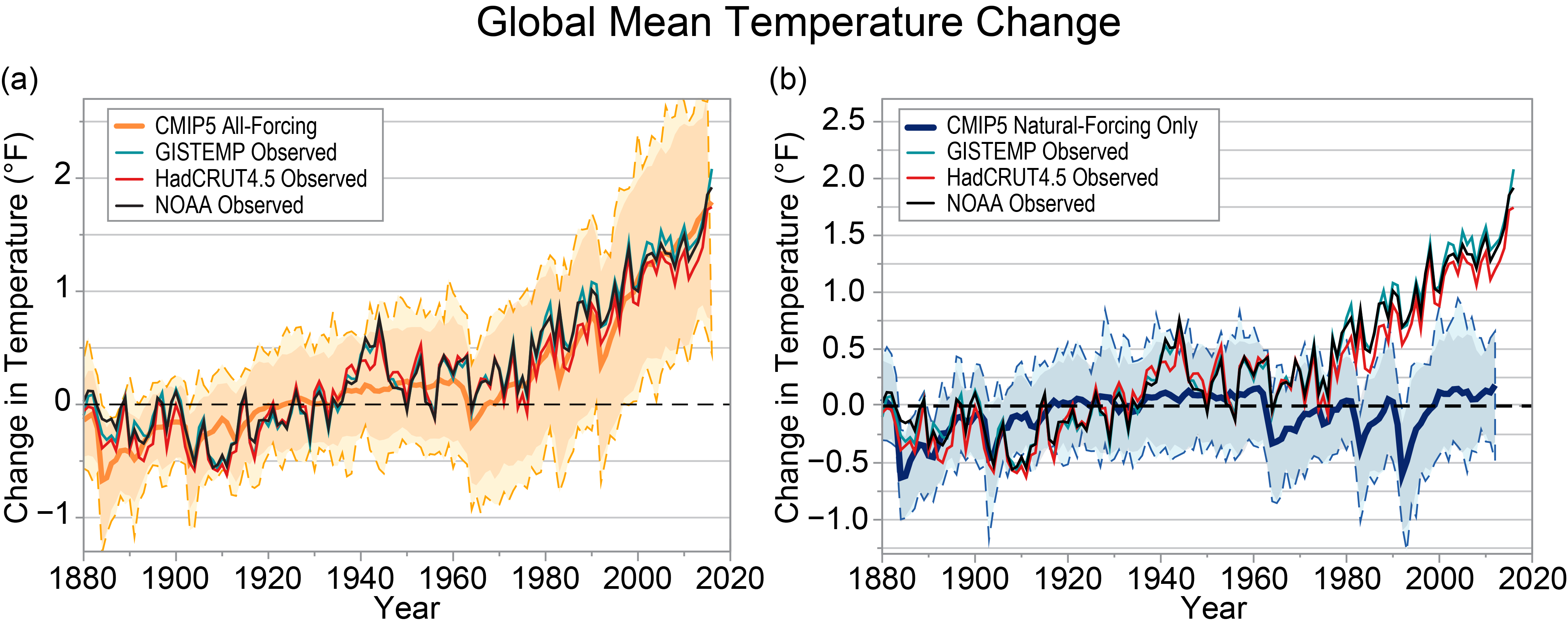
Comparison of observed global mean temperature anomalies from three observational datasets to CMIP5 climate model historical experiments using: (a) anthropogenic and natural forcings combined, or (b) natural forcings only. In (a) the thick orange curve is the CMIP5 grand ensemble mean across 36 models while the orange shading and outer dashed lines depict the ±2 standard deviation and absolute ranges of annual anomalies across all individual simulations of the 36 models. Model data are a masked blend of surface air temperature over land regions and sea surface temperature over ice-free ocean regions to be more consistent with observations than using surface air temperature alone. All time series (°F) are referenced to a 1901–1960 baseline value. The simulations in (a) have been extended from 2006 through 2016 using projections under the higher scenario (RCP8.5). (b) As in (a) but the blue curves and shading are based on 18 CMIP5 models using natural forcings only. See legends to identify observational datasets. Observations after about 1980 are shown to be inconsistent with the natural forcing-only models (indicating detectable warming) and also consistent with the models that include both anthropogenic and natural forcing, implying that the warming is attributable in part to anthropogenic forcing according to the models. (Figure source: adapted from Melillo et al.2 and Knutson et al.19 ).
The detection and attribution of global temperature change to human causes has been one of the most important and visible findings over the course of the past global climate change scientific assessments by the IPCC. The first IPCC report11 concluded that a human influence on climate had not yet been detected, but judged that “the unequivocal detection of the enhanced greenhouse effect from observations is not likely for a decade or more.” The second IPCC report12 concluded that “the balance of evidence suggests a discernible human influence on climate.” The third IPCC report13 strengthened this conclusion to: “most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the increase of greenhouse gas concentrations.” The fourth IPCC report14 further strengthened the conclusion to: “Most of the observed increase in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations.” The fifth IPCC report10 further strengthened this to: “It is extremely likely that more than half of the observed increase in global average surface temperature from 1951 to 2010 was caused by the anthropogenic increase in greenhouse gas concentrations and other anthropogenic forcings together.” These increasingly confident statements have resulted from scientific advances, including better observational datasets, improved models and detection/attribution methods, and improved estimates of climate forcings. Importantly, the continued long-term warming of the global climate system since the time of the first IPCC report and the broad-scale agreement of the spatial pattern of observed temperature changes with climate model projections of greenhouse gas-induced changes as published in the late 1980s (e.g., Stouffer and Manabe 201715 ) give more confidence in the attribution of observed warming since 1951 as being due primarily to human activity.
The IPCC AR5 presented an updated assessment of detection and attribution research at the global to regional scale1 which is briefly summarized here. Key attribution assessment results from IPCC AR5 for global mean temperature are summarized in Figure 3.2, which shows assessed likely ranges and midpoint estimates for several factors contributing to increases in global mean temperature. According to Bindoff et al.,1 the likely range of the anthropogenic contribution to global mean temperature increases over 1951–2010 was 0.6° to 0.8°C (1.1° to 1.4°F), compared with the observed warming 5th to 95th percentile range of 0.59° to 0.71°C (1.1° to 1.3°F). The estimated likely contribution ranges for natural forcing and internal variability were both much smaller (−0.1° to 0.1°C, or −0.2° to 0.2°F) than the observed warming. The confidence intervals that encompass the extremely likely range for the anthropogenic contribution are wider than the likely range. Using these wider confidence limits, the lower limit of attributable warming contribution range still lies above 50% of the observed warming rate, and thus Bindoff et al.1 concluded that it is extremely likely that more than half of the global mean temperature increase since 1951 was caused by human influence on climate. This assessment concurs with the Bindoff et al.1 assessment of attributable warming and cooling influences.
Figure 3.2

Observed global mean temperature trend (black bar) and attributable warming or cooling influences of anthropogenic and natural forcings over 1951–2010. Observations are from HadCRUT4, along with observational uncertainty (5% to 95%) error bars. 62 Likely ranges (bar-whisker plots) and midpoint values (colored bars) for attributable forcings are from IPCC AR5.1 . GHG refers to well-mixed greenhouse gases, OA to other anthropogenic forcings, NAT to natural forcings, and ANT to all anthropogenic forcings combined. Likely ranges are broader for contributions from well-mixed greenhouse gases and for other anthropogenic forcings, assessed separately, than for the contributions from all anthropogenic forcings combined, as it is more difficult to quantitatively constrain the separate contributions of the various anthropogenic forcing agents. (Figure source: redrawn from Bindoff et al.;1 © IPCC. Used with permission.)
Apart from formal detection attribution studies such as those underlying the results above, which use global climate model output and pattern-based regression methods, anthropogenic influences on global mean temperature can also be estimated using simpler empirical models, such as multiple linear regression/energy balance models (e.g., Canty et al. 201316 ; Zhou and Tung 201317 ). For example, Figure 3.3 illustrates how the global mean surface temperature changes since the late 1800s can be decomposed into components linearly related to several forcing variables (anthropogenic forcing, solar variability, volcanic forcing, plus an internal variability component, here related to El Niño–Southern Oscillation). Using this approach, Canty et al.16 also infer a substantial contribution of anthropogenic forcing to the rise in global mean temperature since the late 1800s. Stern and Kaufmann18 use another method—Granger causality tests—and again infer that “human activity is partially responsible for the observed rise in global temperature and that this rise in temperature also has an effect on the global carbon cycle.” They also conclude that anthropogenic sulfate aerosol effects may only be about half as large as inferred in a number of previous studies.
Multi-century to multi-millennial-scale climate model integrations with unchanging external forcing provide a means of estimating potential contributions of internal climate variability to observed trends. Bindoff et al.1 conclude, based on multimodel assessments, that the likely range contribution of internal variability to observed trends over 1951–2010 is about ±0.2°F, compared to the observed warming of about 1.2°F over that period. A recent 5,200-year integration of the CMIP5 model having apparently the largest global mean temperature variability among CMIP5 models shows rare instances of multidecadal global warming approaching the observed 1951–2010 warming trend.19 However, even that most extreme model cannot simulate century-scale warming trends from internal variability that approach the observed global mean warming over the past century. According to a multimodel analysis of observed versus CMIP5 modeled global temperature trends (Knutson et al. 201320 , Fig. 7a), the modeled natural fluctuations (forced plus internal) would need to be larger by about a factor of three for even an unusual natural variability episode (95th percentile) to approach the observed trend since 1900. Thus, using present models there is no known source of internal climate variability that can reproduce the observed warming over the past century without including strong positive forcing from anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions (Figure 3.1). The modeled century-scale trend due to natural forcings (solar and volcanic) is also minor (Figure 3.1), so that, using present models, there is no known source of natural variability that can reproduce the observed global warming over the past century. One study21 comparing paleoclimate data with models concluded that current climate models may substantially underestimate regional sea surface temperature variability on multidecadal to multi-centennial timescales, especially at low latitudes. The causes of this apparent discrepancy–whether due to data issues, external forcings/response, or simulated internal variability issues–and its implications for simulations of global temperature variability in climate models remain unresolved. Since Laepple and Huybers21 is a single paleoclimate-based study and focuses on regional, not global mean, temperature variability, we have consequently not modified our conclusions regarding global temperature attribution from those contained in Bindoff et al.,1 although further research on this issue is warranted. In summary, we are not aware of any convincing evidence that natural variability alone could have accounted for the amount and timing of global warming that was observed over the industrial era.
Figure 3.3
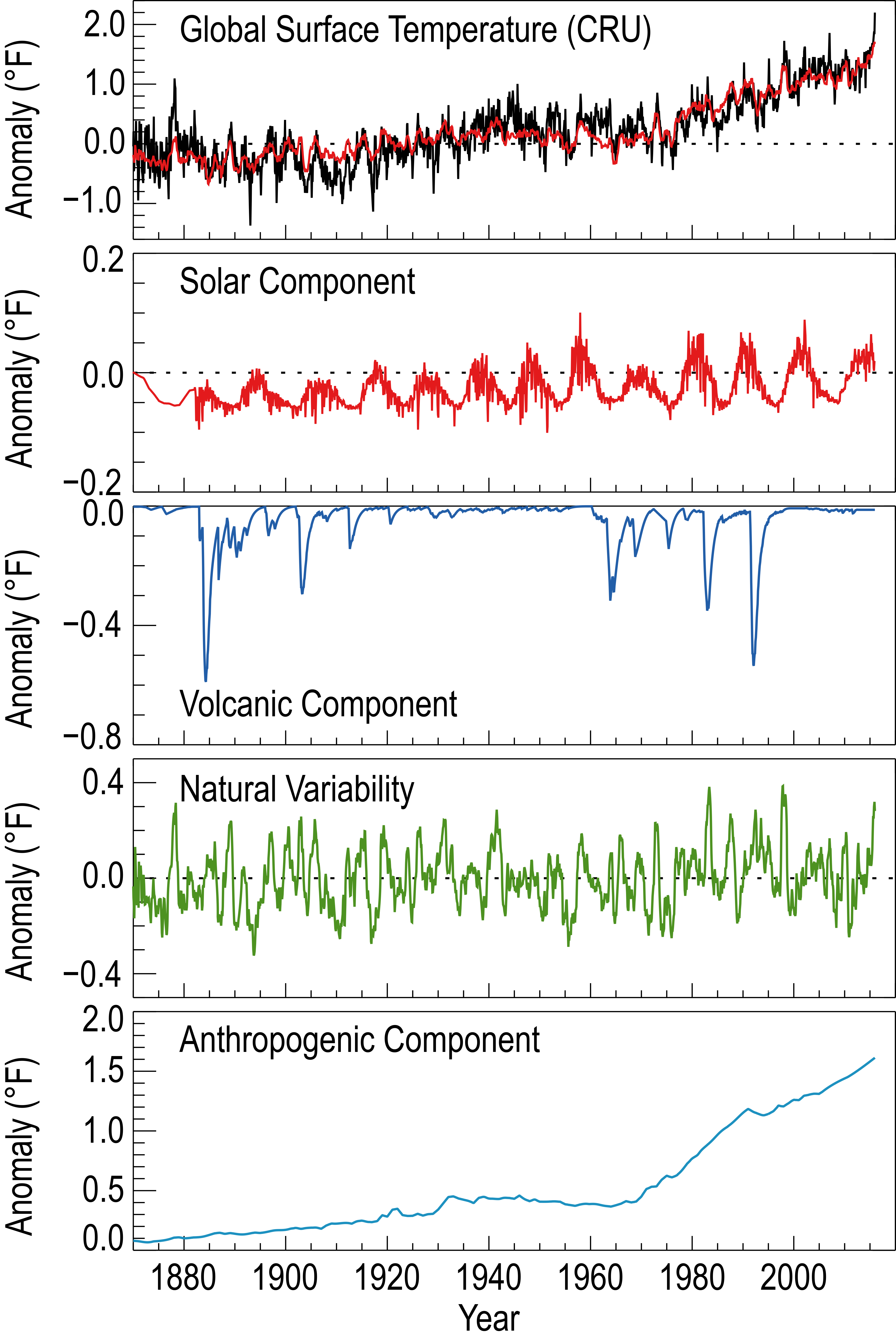
Estimates of the contributions of several forcing factors and internal variability to global mean temperature change since 1870, based on an empirical approach using multiple linear regression and energy balance models. The top panel shows global temperature anomalies (°F) from the observations62 in black with the multiple linear regression result in red (1901–1960 base period). The lower four panels show the estimated contribution to global mean temperature anomalies from four factors: solar variability; volcanic eruptions; internal variability related to El Niño/Southern Oscillation; and anthropogenic forcing. The anthropogenic contribution includes a warming component from greenhouse gases concentrations and a cooling component from anthropogenic aerosols. (Figure source: adapted from Canty et al.16 ).
While most detection and attribution studies focus on changes in temperature and other variables in the historical record since about 1860 or later, some studies relevant to detection and attribution focus on changes over much longer periods. For example, geological and tide-based reconstructions of global mean sea level (Ch. 12: Sea Level Rise, Figure 12.2b) suggest that the rate of sea level rise in the last century was faster than during any century over the past ~2,800 years. As an example, for Northern Hemisphere annual mean temperatures, Schurer et al.22 use detection and attribution fingerprinting methods along with paleoclimate reconstructions and millennial-scale climate model simulations from eight models to explore causes for temperature variations from 850 AD to the present, including the Medieval Climate Anomaly (MCA, around 900 to 1200 AD) and the Little Ice Age (LIA, around 1450 to 1800 AD). They conclude that solar variability and volcanic eruptions were the main causal factors for changes in Northern Hemisphere temperatures from 1400 to 1900, but that greenhouse gas changes of uncertain origin apparently contributed to the cool conditions during 1600–1800. Their study provides further support for previous IPCC report conclusions (e.g., IPCC 200714 ) that internal variability alone was extremely unlikely to have been the cause of the recent observed 50- and 100-year warming trends. Andres and Peltier23 also inferred from millennial-scale climate model simulations that volcanoes, solar variability, greenhouse gases, and orbital variations all contributed significantly to the transition from the MCA to the LIA.
An active and important area of climate research that involves detection and attribution science is the estimation of global climate sensitivity, based on past observational constraints. An important measure of climate sensitivity, with particular relevance for climate projections over the coming decades, is the transient climate response (TCR), defined as the rise in global mean surface temperature at the time of CO2 doubling for a 1% per year transient increase of atmospheric CO2. (Equilibrium climate sensitivity is discussed in Ch. 2: Physical Drivers of Climate Change). The TCR of the climate system has an estimated range of 0.9° to 2.0°C (1.6° to 3.6°F) and 0.9° to 2.5°C (1.6° to 4.5°F), according to two recent assessments (Otto et al.24 and Lewis and Curry25 , respectively). Marvel et al.26 suggest, based on experiments with a single climate model, that after accounting for the different efficacies of various historical climate forcing agents, the TCR could be adjusted upward from the Otto et al.24 and Lewis and Curry25 estimates. Richardson et al.27 report a best estimate for TCR of 1.66°C (2.99 °F), with a 5% to 95% confidence range of 1.0° to 3.3°C (1.8° to 5.9°F). Furthermore, Richardson et al. conclude that the earlier studies noted above may underestimate TCR because the surface temperature dataset they used undersamples rapidly warming regions due to limited coverage and because surface water warms less than surface air. Gregory et al.28 note, within CMIP5 models, that the TCR to the second doubling of CO2 (that is, from doubling to quadrupling) is 40% higher than that for the first doubling. They explore the various physical reasons for this finding and conclude this may also lead to an underestimate of TCR in the empirical observation-based studies. In summary, estimation of TCR from observations continues to be an active area of research with considerable remaining uncertainties, as discussed above. Even the low-end estimates for TCR cited above from some recent studies (about 0.9ºC or 1.6ºF) imply that the climate will continue to warm substantially if atmospheric CO2 concentrations continue to increase over the coming century as projected under a number of future scenarios.
3.3: Detection and Attribution with a United States Regional Focus
Detection and attribution at regional scales is generally more challenging than at the global scale for a number of reasons. At the regional scale, the magnitude of natural variability swings are typically larger than for global means. If the climate change signal is similar in magnitude at the regional and global scales, this makes it more difficult to detect anthropogenic climate changes at the regional scale. Furthermore, there is less spatial pattern information at the regional scale that can be used to distinguish contributions from various forcings. Other forcings that have typically received less attention than greenhouse gases, such as land-use change, could be more important at regional scales than globally.29 Also, simulated internal variability at regional scales may be less reliable than at global scales (Bindoff et al.1 ). While detection and attribution of changes in extremes (including at the regional scale) presents a number of key challenges,7 previous studies (e.g., Zwiers et al. 201130 ) have demonstrated how detection and attribution methods, combined with generalized extreme value distributions, can be used to detect a human influence on extreme temperatures at the regional scale, including over North America.
In IPCC AR5,1 which had a broader global focus than this report, attributable human contributions were reported for warming over all continents except Antarctica. Changes in daily temperature extremes throughout the world; ocean surface and subsurface temperature and salinity sea level pressure patterns; arctic sea ice loss; northern hemispheric snow cover decrease; global mean sea level rise; and ocean acidification were all associated with human activity in AR5.1 IPCC AR5 also reported medium confidence in anthropogenic contributions to increased atmospheric specific humidity, zonal mean precipitation over Northern Hemisphere mid to high latitudes, and intensification of heavy precipitation over land regions. IPCC AR5 had weaker attribution conclusions than IPCC AR4 on some phenomena, including tropical cyclone and drought changes.
Although the present assessment follows most of the IPCC AR5 conclusions on detection and attribution of relevance to the United States, we make some additional attribution assessment statements in the relevant chapters of this report. Among the notable detection and attribution-relevant findings in this report are the following (refer to the listed chapters for further details):
Ch. 5: Circulation and Variability: The tropics have expanded poleward by about 70 to 200 miles in each hemisphere over the period 1979–2009, with an accompanying shift of the subtropical dry zones, midlatitude jets, and storm tracks (medium to high confidence). Human activities have played a role in this change (medium confidence), although confidence is presently low regarding the magnitude of the human contribution relative to natural variability.
Ch. 6: Temperature Change: Detectable anthropogenic warming since 1901 has occurred over the western and northern regions of the contiguous United States according to observations and CMIP5 models (medium confidence), although over the southeastern United States there has been no detectable warming trend since 1901. The combined influence of natural and anthropogenic forcings on temperature extremes have been detected over large subregions of North America (medium confidence).
Ch. 7: Precipitation Change: For the continental United States, there is high confidence in the detection of extreme precipitation increases, while there is low confidence in attributing the extreme precipitation changes purely to anthropogenic forcing. There is stronger evidence for a human contribution (medium confidence) when taking into account process-based understanding (for example, increased water vapor in a warmer atmosphere).
Ch. 8: Drought, Floods, and Wildfire: While by some measures drought has decreased over much of the continental United States in association with long-term increases in precipitation, neither the precipitation increases nor inferred drought decreases have been confidently attributed to anthropogenic forcing. Detectable changes—a mix of increases and decreases—in some classes of flood frequency have occurred in parts of the United States, although attribution studies have not established a robust connection between increased riverine flooding and human-induced climate change. There is medium confidence for a human-caused climate change contribution to increased forest fire activity in Alaska in recent decades and low to medium confidence for a detectable human climate change contribution in the western United States.
Ch. 9: Extreme Storms: There is broad agreement in the literature that human factors (greenhouse gases and aerosols) have had a measurable impact on the observed oceanic and atmospheric variability in the North Atlantic, and there is medium confidence that this has contributed to the observed increase in Atlantic hurricane activity since the 1970s. There is no consensus on the relative magnitude of human and natural influences on past changes in hurricane activity.
Ch. 10: Land Cover: Modifications to land use and land cover due to human activities produce changes in surface albedo, latent and sensible heat, and atmospheric aerosol and greenhouse gas concentrations, accounting for an estimated 40% ± 16% of the human-caused global radiative forcing from 1850 to 2010 (high confidence).
Ch. 11: Arctic Changes: It is very likely that human activities have contributed to observed arctic surface temperature warming, sea ice loss, glacier mass loss, and Northern Hemisphere snow extent decline (high confidence).
Ch. 12: Sea Level Rise: Human-caused climate change has made a substantial contribution to global mean sea level rise since 1900 (high confidence), contributing to a rate of rise that is greater than during any preceding century in at least 2,800 years (medium confidence).
Ch. 13: Ocean Changes: The world’s oceans have absorbed about 93% of the excess heat caused by greenhouse warming since the mid-20th Century. The world’s oceans are currently absorbing more than a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted to the atmosphere annually from human activities, making them more acidic (very high confidence).
3.4: Extreme Event Attribution
Since the IPCC AR5 and NCA3,2 the attribution of extreme weather and climate events has been an emerging area in the science of detection and attribution. Attribution of extreme weather events under a changing climate is now an important and highly visible aspect of climate science. As discussed in the recent National Academy of Sciences report,5 the science of event attribution is rapidly advancing, including the understanding of the mechanisms that produce extreme events and the rapid progress in development of methods used for event attribution.
When an extreme weather event occurs, the question is often asked: was this event caused by climate change? A generally more appropriate framing for the question is whether climate change has altered the odds of occurrence of an extreme event like the one just experienced. Extreme event attribution studies to date have generally been concerned with answering the latter question. In recent developments, Hannart et al.31 discuss the application of causal theory to event attribution, including discussion of conditions under which stronger causal statements can be made, in principle, based on theory of causality and distinctions between necessary and sufficient causality.
Several recent studies, including NAS,5 have reviewed aspects of extreme event attribution.3 ,4 ,6 Hulme4 and NAS5 discuss the motivations for scientists to be pursuing extreme event attribution, including the need to inform risk management and adaptation planning. Hulme4 categorizes event attribution studies/statements into general types, including those based on: physical reasoning, statistical analysis of time series, fraction of attributable risk (FAR) estimation (discussed in the Appendix), or those that rely on the philosophical argument that there are no longer any purely natural weather events. The NAS5 report outlines two general approaches to event attribution: 1) using observations to estimate a change in probability of magnitude of events, or 2) using model simulations to compare an event in the current climate versus that in a hypothetical “counterfactual” climate not influenced by human activities. As discussed by Trenberth et al.,32 Shepherd,33 and Horton et al.,34 an ingredients-based or conditional attribution approach can also be used, when one examines the impact of certain environmental changes (for example, greater atmospheric moisture) on the character of an extreme event using model experiments, all else being equal. Further discussion of methodologies is given in Appendix C.
Examples of extreme event attribution studies are numerous. Many are cited by Hulme,4 NAS,5 Easterling et al.,3 and there are many further examples in an annual collection of studies of extreme events of the previous year, published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.35 ,36 ,37 ,38 ,39
While an extensive review of extreme event attribution is beyond the scope of this report, particularly given the recent publication of several assessments or review papers on the topic, some general findings from the more comprehensive NAS5 report are summarized here:
Confidence in attribution findings of anthropogenic influence is greatest for extreme events that are related to an aspect of temperature, followed by hydrological drought and heavy precipitation, with little or no confidence for severe convective storms or extratropical storms.
Event attribution is more reliable when based on sound physical principles, consistent evidence from observations, and numerical models that can replicate the event.
Statements about attribution are sensitive to the way the questions are posed (that is, framing).
Assumptions used in studies must be clearly stated and uncertainties estimated in order for a clear, unambiguous interpretation of an event attribution to be possible.
The NAS report noted that uncertainties about the roles of low-frequency natural variability and confounding factors (for example, the effects of dams on flooding) could be sources of difficulties in event attribution studies. In addition, the report noted that attribution conclusions would be more robust in cases where observed changes in the event being examined are consistent with expectations from model-based attribution studies. The report endorsed the need for more research to improve understanding of a number of important aspects of event attribution studies, including physical processes, models and their capabilities, natural variability, reliable long-term observational records, statistical methods, confounding factors, and future projections of the phenomena of interest.
As discussed in Appendix C: Detection and Attribution Methodologies, confidence is typically lower for an attribution-without-detection statement than for an attribution statement accompanied by an established, detectable anthropogenic influence (for example, a detectable and attributable long-term trend or increase in variability) for the phenomenon itself. An example of the former would be stating that a change in the probability or magnitude of a heat wave in the southeastern United States was attributable to rising greenhouse gases, because there has not been a detectable century-scale trend in either temperature or temperature variability in this region (e.g., Ch. 6: Temperature Change; Knutson et al. 201320 ).
To our knowledge, no extreme weather event observed to date has been found to have zero probability of occurrence in a preindustrial climate, according to climate model simulations. Therefore, the causes of attributed extreme events are a combination of natural variations in the climate system compounded (or alleviated) by the anthropogenic change to the climate system. Event attribution statements quantify the relative contribution of these human and natural causal factors. In the future, as the climate change signal gets stronger compared to natural variability, humans may experience weather events which are essentially impossible to simulate in a preindustrial climate. This is already becoming the case at large time and spatial scales, where for example the record global mean surface temperature anomaly observed in 2016 (relative to a 1901–1960 baseline) is essentially impossible for global climate models to reproduce under preindustrial climate forcing conditions (for example, see Figure 3.1).
The European heat wave of 200340 and Australia’s extreme temperatures and heat indices of 2013 (e.g., Arblaster et al. 201441 ; King et al. 201442 ; Knutson et al. 201443 ; Lewis and Karoly 201444 ; Perkins et al. 201445 ) are examples of extreme weather or climate events where relatively strong evidence for a human contribution to the event has been found. Similarly, in the United States, the science of event attribution for weather and climate extreme events has been actively pursued since the NCA3. For example, for the case of the recent California drought, investigators have attempted to determine, using various methods discussed in this chapter, whether human-caused climate change contributed to the event (see discussion in Ch. 8: Droughts, Floods, and Wildfires).
As an example, illustrating different methods of attribution for an event in the United States, Hoerling et al.46 concluded that the 2011 Texas heat wave/meteorological drought was primarily caused by antecedent and concurrent negative rainfall anomalies due mainly to natural variability and the La Niña conditions at the time of the event, but with a relatively small (not detected) warming contribution from anthropogenic forcing. The anthropogenic contribution nonetheless doubled the chances of reaching a new temperature record in 2011 compared to the 1981–2010 reference period, according to their study. Rupp et al.,47 meanwhile, concluded that extreme heat events in Texas were about 20 times more likely for 2008 La Niña conditions than similar conditions during the 1960s. This pair of studies illustrates how the framing of the attribution question can matter. For example, the studies used different baseline reference periods to determine the magnitude of anomalies, which can also affect quantitative conclusions, since using an earlier baseline period typically results in larger magnitude anomalies (in a generally warming climate). The Hoerling et al. analysis focused on both what caused most of the magnitude of the anomalies as well as changes in probability of the event, whereas Rupp et al. focused on the changes in the probability of the event. Otto et al.48 showed for the case of the Russian heat wave of 2010 how a different focus of attribution (fraction of anomaly explained vs. change in probability of occurrence over a threshold) can give seemingly conflicting results, yet have no real fundamental contradiction. In the illustrative case for the 2011 Texas heat/drought, we conclude that there is medium confidence that anthropogenic forcing contributed to the heat wave, both in terms of a small contribution to the anomaly magnitude and a significant increase in the probability of occurrence of the event.
In this report, we do not assess or compile all individual weather or climate extreme events for which an attributable anthropogenic climate change has been claimed in a published study, as there are now many such studies that provide this information. Some event attribution-related studies that focus on the United States are discussed in more detail in Chapters 6–9, which primarily examine phenomena such as precipitation extremes, droughts, floods, severe storms, and temperature extremes. For example, as discussed in Chapter 6: Temperature Change (Table 6.3), a number of extreme temperature events (warm anomalies) in the United States have been partly attributed to anthropogenic influence on climate.
References
- Andres, H. J., and W. R. Peltier, 2016: Regional influences of natural external forcings on the transition from the Medieval Climate Anomaly to the Little Ice Age. Journal of Climate, 29, 5779–5800, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-15-0599.1. ↩
- Arblaster, J. M., E.-P. Lim, H. H. Hendon, B. C. Trewin, M. C. Wheeler, G. Liu, and K. Braganza, 2014: Understanding Australia’s hottest September on record [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95 (9), S37–S41, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Bindoff, N. L., P. A. Stott, K. M. AchutaRao, M. R. Allen, N. Gillett, D. Gutzler, K. Hansingo, G. Hegerl, Y. Hu, S. Jain, I. I. Mokhov, J. Overland, J. Perlwitz, R. Sebbari, and X. Zhang, 2013: Detection and attribution of climate change: From global to regional. T.F. Stocker, D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex, and P.M. Midgley, Eds., Cambridge University Press, 867–952. URL ↩
- Canty, T., N. R. Mascioli, M. D. Smarte, and R. J. Salawitch, 2013: An empirical model of global climate – Part 1: A critical evaluation of volcanic cooling. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 3997–4031, doi:10.5194/acp-13-3997-2013. ↩
- Easterling, D. R., K. E. Kunkel, M. F. Wehner, and L. Sun, 2016: Detection and attribution of climate extremes in the observed record. Weather and Climate Extremes, 11, 17–27, doi:10.1016/j.wace.2016.01.001. ↩
- Flato, G., J. Marotzke, B. Abiodun, P. Braconnot, S. C. Chou, W. Collins, P. Cox, F. Driouech, S. Emori, V. Eyring, C. Forest, P. Gleckler, E. Guilyardi, C. Jakob, V. Kattsov, C. Reason, and M. Rummukainen, 2013: Evaluation of climate models. T.F. Stocker, D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex, and P.M. Midgley, Eds., Cambridge University Press, 741–866. URL ↩
- Gregory, J. M., T. Andrews, and P. Good, 2015: The inconstancy of the transient climate response parameter under increasing CO 2. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 373, 20140417, doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0417. ↩
- Hannart, A., J. Pearl, F. E. L. Otto, P. Naveau, and M. Ghil, 2016: Causal counterfactual theory for the attribution of weather and climate-related events. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 97, 99–110, doi:10.1175/bams-d-14-00034.1. ↩
- Herring, S. C., A. Hoell, M. P. Hoerling, J. P. Kossin, C. J. Schreck III, and P. A. Stott, 2016: Explaining Extreme Events of 2015 from a Climate Perspective. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 97, S1–S145, doi:10.1175/BAMS-ExplainingExtremeEvents2015.1. ↩
- Herring, S. C., M. P. Hoerling, J. P. Kossin, T. C. Peterson, and P. A. Stott, 2015: Explaining Extreme Events of 2014 from a Climate Perspective. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 96, S1–S172, doi:10.1175/BAMS-ExplainingExtremeEvents2014.1. ↩
- Herring, S. C., M. P. Hoerling, T. C. Peterson, and P. A. Stott, 2014: Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95, S1–S104, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Hoerling, M., M. Chen, R. Dole, J. Eischeid, A. Kumar, J. W. Nielsen-Gammon, P. Pegion, J. Perlwitz, X.-W. Quan, and T. Zhang, 2013: Anatomy of an extreme event. Journal of Climate, 26, 2811–2832, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00270.1. ↩
- Horton, R. M., J. S. Mankin, C. Lesk, E. Coffel, and C. Raymond, 2016: A review of recent advances in research on extreme heat events. Current Climate Change Reports, 2, 242–259, doi:10.1007/s40641-016-0042-x. ↩
- Hulme, M., 2014: Attributing weather extremes to “climate change.” Progress in Physical Geography, 38, 499–511, doi:10.1177/0309133314538644. ↩
- IPCC, 1990: Climate Change: The IPCC Scientific Assessment. Cambridge University Press, 212 pp. ↩
- IPCC, 1996: Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group I to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, 584 pp. ↩
- IPCC, 2001: Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, 881 pp. ↩
- IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor, and H.L. Miller, Eds. Cambridge University Press, 996 pp. URL ↩
- IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 1535 pp., Cambridge University Press. ↩
- King, A. D., D. J. Karoly, M. G. Donat, and L. V. Alexander, 2014: Climate change turns Australia’s 2013 Big Dry into a year of record-breaking heat [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95 (9), S41–S45, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Knutson, T. R., F. Zeng, and A. T. Wittenberg, 2013: Multimodel assessment of regional surface temperature trends: CMIP3 and CMIP5 twentieth-century simulations. Journal of Climate, 26, 8709–8743, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00567.1. ↩
- Knutson, T. R., F. Zeng, and A. T. Wittenberg, 2014: Multimodel assessment of extreme annual-mean warm anomalies during 2013 over regions of Australia and the western tropical Pacific [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95 (9), S26–S30, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Knutson, T. R., R. Zhang, and L. W. Horowitz, 2016: Prospects for a prolonged slowdown in global warming in the early 21st century. Nature Communcations, 7, 13676, doi:10.1038/ncomms13676. ↩
- Laepple, T., and P. Huybers, 2014: Ocean surface temperature variability: Large model–data differences at decadal and longer periods. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111, 16682–16687, doi:10.1073/pnas.1412077111. ↩
- Lewis, N., and J. A. Curry, 2015: The implications for climate sensitivity of AR5 forcing and heat uptake estimates. Climate Dynamics, 45, 1009–1023, doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2342-y. ↩
- Lewis, S., and D. J. Karoly, 2014: The role of anthropogenic forcing in the record 2013 Australia-wide annual and spring temperatures [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95 (9), S31–S33, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Marvel, K., G. A. Schmidt, R. L. Miller, and L. S. Nazarenko, 2016: Implications for climate sensitivity from the response to individual forcings. Nature Climate Change, 6, 386–389, doi:10.1038/nclimate2888. ↩
- Melillo, J. M., T. (T. C. . Richmond, and G. W. Yohe, eds., 2014: Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment. U.S. Global Change Research Program, 841 pp. ↩
- Morice, C. P., J. J. Kennedy, N. A. Rayner, and P. D. Jones, 2012: Quantifying uncertainties in global and regional temperature change using an ensemble of observational estimates: The HadCRUT4 dataset. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117, D08101, doi:10.1029/2011JD017187. ↩
- NAS, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change. The National Academies Press, 186 pp. ↩
- Otto, A., F. E. L. Otto, O. Boucher, J. Church, G. Hegerl, P. M. Forster, N. P. Gillett, J. Gregory, G. C. Johnson, R. Knutti, N. Lewis, U. Lohmann, J. Marotzke, G. Myhre, D. Shindell, B. Stevens, and M. R. Allen, 2013: Energy budget constraints on climate response. Nature Geoscience, 6, 415–416, doi:10.1038/ngeo1836. ↩
- Otto, F. E. L., N. Massey, G. J. van Oldenborgh, R. G. Jones, and M. R. Allen, 2012: Reconciling two approaches to attribution of the 2010 Russian heat wave. Geophysical Research Letters, 39, L04702, doi:10.1029/2011GL050422. ↩
- Perkins, S. E., S. C. Lewis, A. D. King, and L. V. Alexander, 2014: Increased simulated risk of the hot Australian summer of 2012/13 due to anthropogenic activity as measured by heat wave frequency and intensity [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95 (9), S34–S37, doi:10.1175/1520-0477-95.9.S1.1. ↩
- Peterson, T. C., M. P. Hoerling, P. A. Stott, and S. C. Herring, 2013: Explaining Extreme Events of 2012 from a Climate Perspective. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 94, S1–S74, doi:10.1175/bams-d-13-00085.1. ↩
- Peterson, T. C., P. A. Stott, and S. Herring, 2012: Explaining extreme events of 2011 from a climate perspective. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93, 1041–1067, doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00021.1. ↩
- Pielke Sr., R. A., R. Mahmood, and C. McAlpine, 2016: Land’s complex role in climate change. Physics Today, 69, 40–46, doi:10.1063/PT.3.3364. ↩
- Richardson, M., K. Cowtan, E. Hawkins, and M. B. Stolpe, 2016: Reconciled climate response estimates from climate models and the energy budget of Earth. Nature Climate Change, 6, 931–935, doi:10.1038/nclimate3066. ↩
- Rupp, D. E., P. W. Mote, N. Massey, C. J. Rye, R. Jones, and M. R. Allen, 2012: Did human influence on climate make the 2011 Texas drought more probable? [in “Explaining Extreme Events of 2011 from a Climate Perspective”]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93, 1052–1054, doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00021.1. ↩
- Schurer, A. P., G. C. Hegerl, M. E. Mann, S. F. B. Tett, and S. J. Phipps, 2013: Separating forced from chaotic climate variability over the past millennium. Journal of Climate, 26, 6954–6973, doi:10.1175/jcli-d-12-00826.1. ↩
- Shepherd, T. G., 2016: A common framework for approaches to extreme event attribution. Current Climate Change Reports, 2, 28–38, doi:10.1007/s40641-016-0033-y. ↩
- Stern, D. I., and R. K. Kaufmann, 2014: Anthropogenic and natural causes of climate change. Climatic Change, 122, 257–269, doi:10.1007/s10584-013-1007-x. ↩
- Stone, D., M. Auffhammer, M. Carey, G. Hansen, C. Huggel, W. Cramer, D. Lobell, U. Molau, A. Solow, L. Tibig, and G. Yohe, 2013: The challenge to detect and attribute effects of climate change on human and natural systems. Climatic Change, 121, 381–395, doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0873-6. ↩
- Stott, P. A., D. A. Stone, and M. R. Allen, 2004: Human contribution to the European heatwave of 2003. Nature, 432, 610–614, doi:10.1038/nature03089. ↩
- Stott, P., 2016: How climate change affects extreme weather events. Science, 352, 1517–1518, doi:10.1126/science.aaf7271. ↩
- Stouffer, R. J., and S. Manabe, 2017: Assessing temperature pattern projections made in 1989. Nature Climate Change, 7, 163–165, doi:10.1038/nclimate3224. ↩
- Trenberth, K. E., J. T. Fasullo, and T. G. Shepherd, 2015: Attribution of climate extreme events. Nature Climate Change, 5, 725–730, doi:10.1038/nclimate2657. ↩
- Zhou, J., and K.-K. Tung, 2013: Deducing multidecadal anthropogenic global warming trends using multiple regression analysis. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 70, 3–8, doi:10.1175/jas-d-12-0208.1. ↩
- Zwiers, F. W., L. V. Alexander, G. C. Hegerl, T. R. Knutson, J. P. Kossin, P. Naveau, N. Nicholls, C. Schär, S. I. Seneviratne, and X. Zhang, 2013: Climate extremes: Challenges in estimating and understanding recent changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme climate and weather events. G.R. Asrar and J.W. Hurrell, Eds., Springer Netherlands, 339–389. ↩
- Zwiers, F. W., X. B. Zhang, and Y. Feng, 2011: Anthropogenic influence on long return period daily temperature extremes at regional scales. Journal of Climate, 24, 881–892, doi:10.1175/2010jcli3908.1. ↩